In compliance with EU personal data protection laws, we are committed to protecting your personal data.
By clicking "Accept All", you allow us to place cookies to enhance your experience on this site, help us analyze site performance and usage, and enable us to deliver relevant marketing content. You can manage your cookie settings below. By clicking "Accept All" you agree to the current settings.
Risk Management
Risk Management Procedure and Organizational Structure
The “Operational Risk Management Regulations” of the Company was approved by the board of directors in 2014. The “Operational Risk Management Regulations” was established in accordance with the structure of the ISO 31000 standard, and such regulations are served as the operational rules for relevant organizations and supervisors at all levels of the Company to perform operational risk management. It was revised on Dec 23, 2024 and approved by the board of directors.
According to the Operational Risk Management Regulations, the Company has established a Risk Management Committee in the organization in order to perform risk identification for all risks from the internal or external of the organization during the operation process that may cause major operational impact, operation interruption to the Company, or may affect the execution of important strategies, affect achievement of important goals, or may cause violation of laws/regulations, etc., and to perform risk identification, risk assessment, risk response and risk supervision operation along with process and detailed rules, thereby minimizing the probability of occurrence and impact of various types of critical operational risks.
The Company has established a Risk Management Committee with the President acting as the chairperson of the Organization in charge of directing the promotion and operation of risk management plans. Under such Organization, there are various center responsible units in charge of the promotion of various affairs and operations of risk management.
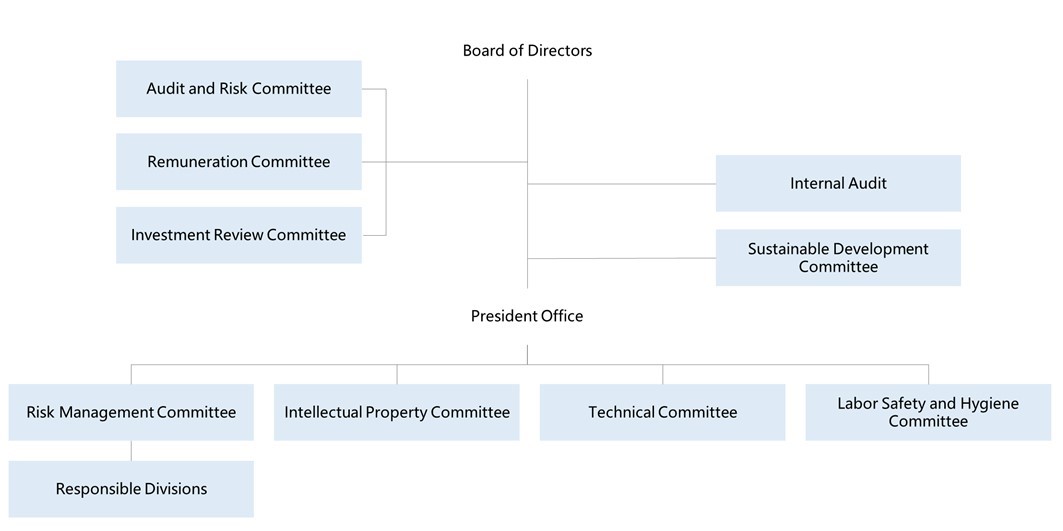
Scope of Risk Management
The risk management meetings of the Company are convened by the President regularly and irregularly for matters related to
(1) Business/Laws/Regulations/Standards
(2) Political Environment
(3) Economic/Financial Environment
(4) Climate Change/Natural Disaster
(5) Technology and Information
(6) Competition Environment
(7) Facility/Equipment
(8) Sales/Market Management
(9) Supply Chain
(10) Financial Operation
(11) Community/Environmental Safety and Health
(12) Internal and External Personnel of the Organization, etc.
There are a total of 12 major categories and 92 indicators for assessment, and mitigation responsive strategies, solutions and operation continuity plans are established to eliminate, reduce, transfer and accept risks, in addition to the enhancement of the pre-warning and monitoring capacity, promotion of risk identification and control, in order to implement appropriate risk management oriented business model, thereby achieving the operational goals and increasing values for shareholders and internal/external related parties.
Annual Operational Risk Management Execution Status
The second regular risk management meeting was held in 2024:
2024.04.17 Risk management regular meeting was convened. (U.S. – China trade and technique conflict / Ukrainian-Russia war and Taiwan strait conflict / ESG promote)
2024.10.02 Risk management regular meeting was convened. (China-own ASIC industrial development / Israel-Hamas war / Exchange Rate / Automotive demand leap / worldwide natural disaster / low risk country production base)
2024.11.04 The 2024 operational risk management execution status was reported in the board of directors meeting.
Risk Management Policy
| Dimension |
Major Issue |
Risk Identification |
Risk Response |
Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corporate Governance |
Sustainability |
The ongoing US-China technology/trade war remains a concern, adding significant uncertainty to the growth and changes in China's consumer and telecommunications industries. |
Mitigate risk impacts |
1. Continuously enhancing the 4-new project. |
| Environmental |
Climate Change Risk and Opportunities |
The risk of supply from suppliers has also increased as climate change exacerbates the situation. |
Mitigate risk impacts |
1. Monitor the various changes in logistics operations and their corresponding solutions. |
| Corporate Governance | Sustainability | Operational risks such as increased minimum wages, rising labor insurance rates, higher electricity costs, and inflation are leading to inevitable production cost increases, which will affect our costs and profits. |
Mitigate risk impacts |
Due to labor shortages, inflation, and geopolitical conflicts, there has been a series of impacts such as rising global supply chain costs, increased labor wages, higher insurance rates, and elevated production costs. To ensure long-term competitiveness and stakeholders' interests, the company is taking the following controllable measures: 1. Continuously investing in advanced technology and new product development to enhance product advantages, improve manufacturing costs, and adjust product mix and profit structure. This aims to prevent cost increases of existing products from affecting overall sales and eroding profits. 2. Promoting the application of digitalization and automation, utilizing artificial intelligence and digital technology to boost per capita productivity and reduce inefficiencies and waste, thereby mitigating the impact of external cost increases. 3. Considering the expansion of production lines in countries or regions with lower production costs to diversify geopolitical supply chain risks and reduce overall production costs. |
| Environmental |
Climate Change Risk and Opportunities |
The recently announced drafts of the three sub-regulations for carbon fees will impact production costs. |
Mitigate risk impacts |
According to the greenhouse gas inventory results, the company's carbon dioxide emissions have not reached the threshold for carbon fee collection, thus there is no immediate carbon fee risk. In 2023, the company signed a CPPA contract with a power supplier to use renewable energy starting in 2024, with an annual target of 10% and a plan to increase this percentage year by year. The company continuously promotes energy conservation and carbon reduction measures each year, aiming to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. Therefore, the risk of climate change is manageable. |
| Corporate Governance |
Sustainability |
Promotion of ESG |
Eliminate risks |
1. Increase resource allocation towards ESG promotion activities. 2. Strengthen ESG-related information disclosure on the company website. |
| Corporate Governance |
Sustainability |
The impact of China accelerating the development of its independent IC industry |
Mitigate risk impacts |
Strengthen relationships with IC design houses and promote "design in" initiatives. |
| Society |
Supplier |
Development of Israel-Hamas war |
Mitigate risk impacts |
Immediately conduct simulations of various logistics scenarios and respond promptly to current events. |
| Corporate Governance |
Sustainability |
Rapid change of exchange rates |
Mitigate risk impacts |
1. Correspond transaction terms with material suppliers. 2. Implement financial risk mitigation measures. |
| Corporate Governance |
Sustainability |
Rapid increase in Automotive demand |
Mitigate risk impacts |
1. Enhance control over long-term customer demand information. 2. Review inventory safety plans. 3. Ensure the new factory expansion and production ramp-up are precisely on schedule to achieve customer certification. |
| Environmental |
Climate Change Risk and Opportunities |
Frequent occurance of natural disasters |
Mitigate risk impacts |
1. Review Safety Stock Agreement with suppliers. 2. Conduct simulations of various logistics scenarios. |
| Society |
Sustainability |
Demand for production sites in low-risk countries |
Eliminate risks |
The progress of expanding to the third and fourth production sites in the project must be completed as scheduled and to the desired quality. |
